QUALITATIVE APPRAISAL QUESTIONS
Student Name:
Instructions: Download this form and answer these questions to systematically evaluate a research study. Type your answers in under each question, leaving a space between the question and your answer. Answer the questions completely and in full sentences. Make sure that you answer each part of the question; if any answer is “no” or not applicable, describe how you came to that conclusion. Correct APA citations are required for each answer. Citations for direct quotes should include page numbers. HINT: Your textbook is an edited “chapter book” with different authors for each chapter, so make sure to use the correct format. You should have two references—this article and your textbook. After you have finished answering the questions, fill out the summary grid with KEY INFORMATION only—bullet points without complete sentences. Your grid should take up no more than one page. This set of questions and the grid is worth 5 points in total.
Introduction
- What was the problem under investigation? In other words, what was the problem that prompted the researchers to complete the research? What was the importance of the problem? To healthcare? To nursing? Do you agree that it’s an important problem to study? Why?
The study was intended to investigate how national clinical audit and feedback about blood transfusion practice is received; disseminated and how such audit and feedback inform response actions (Gould et al., 2018). The problem that informs this study is that, while blood is a crucial product, poor blood transfusion and management are observed in some hospitals, and there are cases where the blood goes bad due to poor handling. According to the World Health Organization, while demand for blood remains very high, unpredictable, and sometimes characterized with spikes, especially during tragedies, disasters, and pandemics, the blood supply is relatively low and constant. It is therefore important to ensure all potentially available blood is conserved and put into meaningful use. No wastages should be witnessed. This requires effective blood transfusion and management practices. To ensure effective transfusion, management, and blood use, world health organization’s advocate for a robust system with inbuilt audits and feedback mechanisms. Clinical audit and feedback are important to nursing practitioners and the health sector as they provide checks and balances in blood transfusion systems.
- REVIEW OF THE LITERATURE – this may be found in a separate section or the introduction or background. What concepts/variables or topics related to the problem were covered in the review of literature? Was the literature review comprehensive, current, and of good quality? In other words, did it look at different aspects of the problem, was it in the scholarly date range for when the study was completed and was it from scholarly journals?
In the current study, the researcher adopted a control theory to contextualize feedback in the hospital environment. Control theory is relevant in this study as it explains how people’s behaviors can be controlled as they receive and act on feedback. The key concepts discussed in this study include feedback reception factors; including reception points and individuals of feedback, transfusion process for feedback to other parties in the hospitals, decision process surrounding audit and feedback, barriers and enablers of implementation of recommendations of audit tools and infrastructure adopted in response and well as the response actions are taken post-audit feedback. Other variables include; social and behavioral factors exhibited in the feedback environment, knowledge, motivation, and belief systems around the post feedback decision environment and implementation process (Gould et al., 2018). The study sources are generally relevant and current, with most sources being research articles not older than ten years.
While the study addressed various aspects of clinical audit and feedback systems, the research concepts are not well discussed in the literature. Literature does not present clearly how the research concepts are operationalized. Similarly, the literature does not provide a direct link to the research objectives and the research topic. A good research must have clear research variables, traceable to the research topic, linked to the research objectives, and comprehensively covered in the research literature. Besides, the literature should be current, from reputable sources, and must capture relevant theories and models in addition to the research concepts.
- If a model/theory/theoretical framework was FORMALLY cited as a basis for the study, what was it? If no model or framework was specifically identified, the state where you looked for it.
At least a model or theory should inform a good study. There should be a separate section in the article that presents the theoretical review or models the study is founded on. The model or theory must be relevant in explaining the relationship between concepts in the study. The current study does not have a model. It, however, has good theoretical ground. The researchers used social influence, behavioral regulation, social and professional roles and identity, nature of behaviors, knowledge, motivation, goals, beliefs about consequences, and decision process as the main theoretical domains. While the theoretical domains look more like research indicators, these domains enabled the researchers to develop more relevant research indicators. Proper operationalization of research variables aid in research questionnaire item development and enhances the research objectives’ achievement.
- QUOTE the research question, aim, or purpose. Identify the MAIN variables that this study will be investigating. Remember, EVERY study investigates variables of interest!
The current study aimed to establish how hospitals receive audit outcomes and respond to feedback relating to blood transfusion practice. The study tried to achieve the aim of the study by focusing on several variables. The study determined who is involved and the level of participation in prescription, transfusion, and whether the participants were aware of the current audit and feedback processes and procedures. The study aimed to identify individuals involved in the initial reception of feedback, the specific actions taken when the feedback is received, and how the feedback is disseminated. The study aimed to establish if and how the staff was involved in the discussion of feedback, and if such discussions were there, whether the discussions were planned and structured if planned, what methods and tools were used in giving response to the feedback given and whether the process is continuous and well monitored. Lastly, the study looked at how decisions relating to audit and feedback were made, what level of involvement is realized, and the proper infrastructure for decision and action plan. While focused on the above concepts to achieve the research objectives, the research variables do not come out as strongly and clearly measurable (Gould et al., 2018).
Design
- What is the specific study design used (ex: grounded theory, phenomenological, descriptive, ethnographic, historical, case study)? Explain this design as described in your text. Don’t forget to cite!
The study used a multiple case study design. Multiple case study design involved data collection from more than one case and using such data to generalize the research population. The design enables the researchers to examine contextual factors about the population making it possible to compare the population based on data collection points. A multiple cases study design just like experimental study design produces straight description and comprehensive summary of the research phenomenon (Schmidt and Brown, 2019).
Methods
- What was the population? What sampling method was used to determine the sample? Were there inclusion and exclusion criteria for the sample listed? How big was the sample (also called the “n” number)? How were the participants recruited? What were the demographic characteristics of the sample? Do the authors state how they determined if the number of participants was adequate to complete the study? What was the setting for the study?
The study sample in the study involved hospitals that routinely take part in NHSBT NCAs of blood transfusion. Purposive sampling was used to select the research sample. Clinical leads and research teams were involved in identifying four hospitals that had a diverse infrastructure. The hospitals were contacted through trust research and development officers. The sample included individuals involved in; prescription of blood components, administration of blood components, and formulation and implementation of response to feedback. The samples ensured representation in terms of gender, role, experience, and involvement in auditing and feedback practices (Gould et al., 2018). While the study clearly explains how sampling was done and who constituted the study respondents, it is not clear the number of respondents involved in the study.
- How were the rights of the participants protected? Was there ethical approval granted for the study? What were some of the risks to the participants? How did the participants consent to participate in the study?
Respondents were formally requested to agree to take part in the study through mails. The respondents who accepted to participate in the study were requested to give formal consent by signing the consent forms. This ensured that no respondent participated against the will. Besides, consent was sought in the hospitals before data collection. The study, however, did not specify how the privacy integrity of information guaranteed.
- How was the study carried out? (Write out in a step-by-step fashion starting with ethical approval through data analysis. Be complete and specific.
The study collected data through semi-structured interviews and a structured observation sheet. Interviews were audio-recorded for analysis. Before data collection, respondents were mailed are requested to take part in the study willingly. This was followed by formal consent signing for those who accepted to be involved in the study. Additional respondents were selected through referrals and recommendations from engaged respondents. The data collection method and procedure used in the study were effective, adequate, and clear.
- Was there any attrition or mortality? Describe your rationale for making this determination that shows your understanding of these terms.
The study did not report any case of mortality (death) or attrition (drop out) rates. However, there was a need for substitution to replace some participants as it was discovered that key participants were not always present in the meetings to discuss and disseminate feedback (Gould et al., 2018).
- What instrument or instruments were used to collect the data for this study? If interviews were used, were the questions open-ended? Were the instruments or questions asked valid and reliable? How do you know?
The study used semi-structured interviews and a structured observation sheet to collect research data. The study used open-ended questions to collect data. Besides, the researchers adopted face to face and one to one interviews with the respondents. Open-ended questions allow respondents to give individualized responses to research items/questions. This is evident in the data collection tools shared in the document.
Data Analysis and Results
- How were the responses of the participants analyzed? List the specific techniques and tests used. List any software products used.
Research data were analyzed along with the themes identified in the previous studies. Emerging themes were verified using the existing themes. The analysis started with the coding of data, after which similar responses were grouped using inductive thematic analysis to generate a label for each thematic area. The domains were then classified based on importance. Observational field notes were used to identify if responses were initiated using HTC meetings. This analysis method was elaborate and robust and therefore yielded sound results.
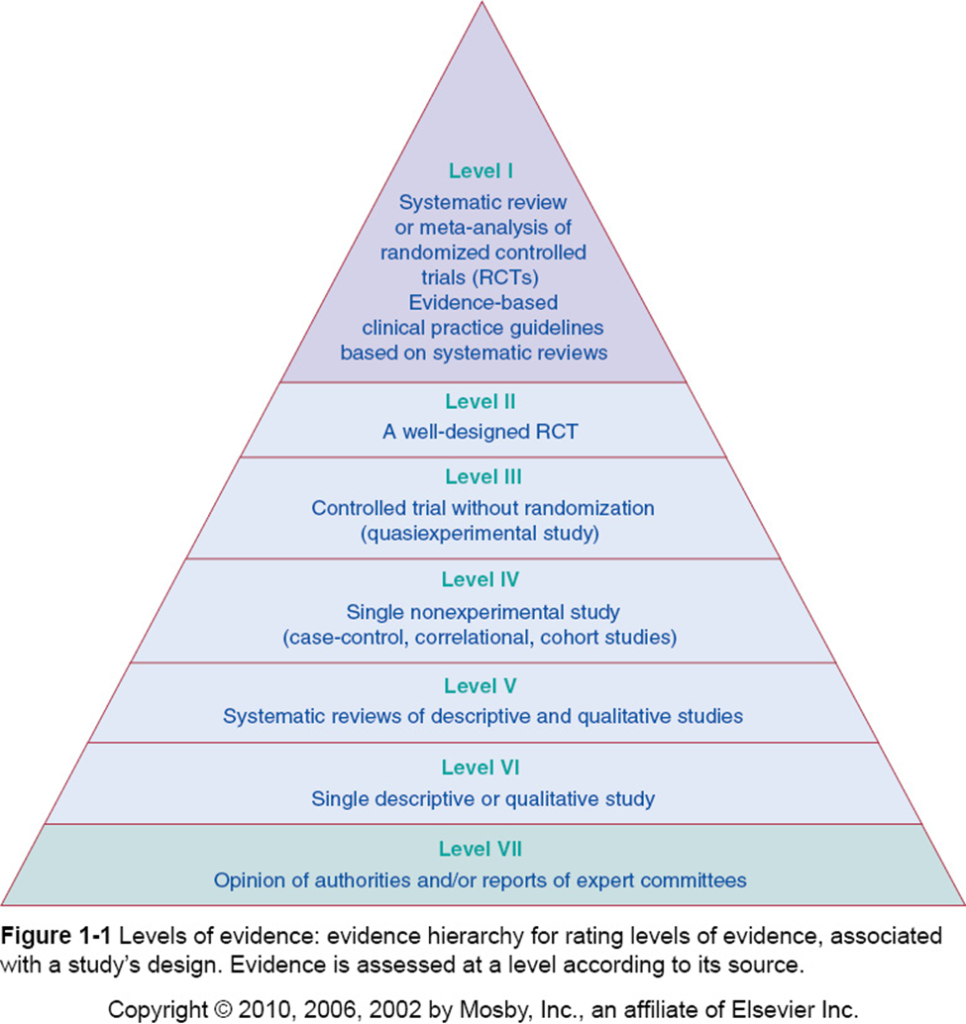
- What were the described findings of the study? Do the findings of the study answer the research question or hypothesis? Using the pyramid provided as a guide, what is the level of evidence for this study?
Findings revealed that staff offering blood transfusion, hematology, transfusion laboratory, and audit facilitation services are the major recipients of feedback from the National Comparative Audit. This team is also the initial respondents to the feedback. When the feedback is received, a team consists of a blood transfusion team, participants from other functional areas of the hospital and audit experts, and patient blood management officers. This team receives feedback through the hospital blood transfusion team. The team may also pass the feedback information to the top management office and other hospital units to guide decision-making and policy formulation concerning blood transfusion and management (Gould et al., 2018).
The study was concerned if there could be challenges experienced when responding to audit feedback. The main challenges reported in existing empirical literature include; inadequate staff, not giving priority to audit feedback, not considering the audit reports as important as the aught to be, and sometimes lacking adequate capacity in terms of response tools and infrastructure. The slow and poor decision process, poor time management, lack of clarity of purpose, rushed decisions, lack of motivation, insufficient knowledge, and capacity, as well as lack of goodwill, have also been identified as major hindrances in response to audit feedback (Gould et al., 2018).
A question was raised on the enabling factors in response to audit feedback. Literature indicates that clarity and unity of purpose, collaborative approach to decisions and actions, effective empowerment and motivation, knowledge enhanced through training, and empowerment through appropriate tools and infrastructure (Gould et al., 2018). These findings relate to the topic and provide answers to the research questions. The researchers tried to be as objective as possible.
Discussion/Conclusions
- Do the authors seem to interpret their findings correctly in the discussion and conclusion? Is the discussion of the findings and implications for applying the findings strictly limited to the study’s information, or do they add in their own opinions? Is there any evidence of bias in the study?
Generally, the findings are well interpreted; the findings inform the conclusions drawn from the findings. The research conclusion is significantly free from bias. Similarly, recommendations made from the study are informed by the findings.

ORDER A CUSTOM ESSAY NOW
HIRE ESSAY TYPERS AND ENJOT EXCELLENT GRADES
- How do these results compare to others (in the original literature review and/or later studies? Do they align with previously conducted research or disagree with it?
The findings of this study are consistent with the findings of other studies and published literature, which also suggest that national clinical audit is critical for health care and driving system-wide change. The effect of audit and feedback according to study depend on a range of variables, including staff receiving the feedback and response or staff regulating their behavior as required. The article emphasized on evidence-based practice to enhance care, which is in alignment with (Schmidt & Brown, 2019).
- What limitations were identified by the authors? Did you discover any other limitations throughout your appraisal that were NOT cited by the authors?
The first limitation is that this study was quite sensitive in terms of the research data sought. Respondents were, therefore, likely to be unwilling to give the required research data. The researchers were proactive in the way data collection was approached by seeking consent from respondents and the hospitals before data collection.
- Did the authors list any implications for nursing care, other improvements to healthcare, or future research?
The study suggested that the findings could inform strategies that can be adopted to enhance the effectiveness of audit and feedback responses in hospitals.
Application
- Does this study offer any benefit to society or healthcare at large? Does this study investigate topics that would be of interest to patients or other stakeholders? What patient preferences (if any) might you need to consider before applying the findings from this study? Describe your rationale for making this determination.
The study’s findings are likely to be useful in decision-making and strategy formulation relating to blood transfusion practices. The findings could also inform decisions around the planning and execution of response action.
- Was the study trustworthy (as defined in your text)? Is it transferable? If so, to which populations? In your opinion, do the overall strengths of this study outweigh its limitations?
The study adopted sound scientific tools. It was founded on relevant theories. Data was collected using sound, valid and reliable tools. Besides, the research data were analyzed using sound statistical tools. Lastly, the research conclusions were made from the research findings. The study was generally of good quality.
References
Gould, N., Lorencatto, F., During, C., Rowley, M., Glodwell, L., Walwyn, R., et al. (2018). How do hospitals respond to feedback about blood transfusion practice? A multiple case study investigation. PLoS ONE, 13(11).
Schmidt, N. A., & Brown, J. M. (2019). Evidence-based practice for nurses: appraisal and application of research. Jones & Bartlett Learning.

- FAST HOMEWORK HELP
- HELP FROM TOP TUTORS
- ZERO PLAGIARISM
- NO AI USED
- SECURE PAYMENT SYSTEM
- PRIVACY GUARANTEED
SEE NEXT PAGES FOR GRID AND EVIDENCE PYRAMID.
Make sure to delete the instructions on the grid after you have used them to make sure that your grid fits on one sheet of paper. If you have too much information, you will need to edit it!
| Research Problem, Question/ Purpose | Sample/ Setting | Study Design/ Methods | Variables | Results/Conclusion Outcomes | Limitations/ Strengths | Level of Evidence |
| To determine who is involved and the level of participation of participants in prescription, transfusion and whether the participants were aware of the current audit and feedback processes and procedures; to establish if and how staff were involved in the discussion of feedback, and if such discussions were there, whether the discussions were planned and structured | Purposive sampling was used to select the research sample. Clinical leads and research teams were involved in identifying four hospitals that had a diverse infrastructure. The hospitals were contacted through trust research and development officers. The sample included individuals involved in; prescription of blood component, administration of blood components, and formulation and implementation of response to feedback | The study used multiple case study design to examine contextual factors about the population making it possible to compare the population based on data collection points | The study used semi-structured interviews and a structured observation sheet to collect research data. The study used open-ended questions to collect data. Besides, the researchers adopted face to face and one to one interviews with the respondents | Staff offering blood transfusion, hematology, transfusion laboratory, and audit facilitation services are the major recipients of feedback from the National Comparative Audit The main challenges reported in existing empirical literature include; inadequate staff, not giving priority to audit feedback, not considering the audit reports as important as the aught to be, and sometimes lack adequate capacity Clarity and unity of purpose, collaborative approach to decisions and actions, effective empowerment and motivation, knowledge enhanced through training and empowerment through appropriate tools and infrastructure are the main enablers | Sensitive in terms of research data sought was a limitation Robustness of methodology was a strength | Level I |
Use this grid to determine the level of evidence